Mastering the art of describing line graphs is an essential skill for IELTS Writing Task 1. This task requires you to accurately interpret and present data in a clear and concise manner, showcasing your ability to convey complex information in English. A well-structured and detailed response can significantly boost your overall writing score.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of writing about line graphs, exploring proven strategies and techniques to help you achieve a Band 9 in your IELTS Writing exam. From understanding the nuances of line graphs to crafting a compelling and insightful report, this guide will equip you with the necessary tools to succeed.
Understanding Line Graphs in IELTS Writing
Line graphs, also referred to as line charts, visually represent data points connected by lines over a specific timeframe. They effectively illustrate trends, fluctuations, and patterns in data. In the IELTS Writing Task 1, you may be presented with a single line graph or multiple line graphs to analyze and describe.
Key Components of a Line Graph:
- Vertical Axis (Y-axis): Typically represents the measurement or variable being depicted, such as population, temperature, or sales figures.
- Horizontal Axis (X-axis): Usually represents the time period, which can be years, months, or any other time unit.
- Data Points: Individual values on the graph, marked as points, that represent specific data points.
- Lines: Connect the data points, visually showing the changes in data over time.
- Legend (if applicable): Provides a clear explanation of the different lines on the graph, especially when multiple lines are present.
Crafting a Band 9 Line Graph Report
Writing a high-scoring line graph report requires a structured approach and careful attention to detail. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you craft a compelling response:
1. Analyze the Graph and Identify Key Features
Before you begin writing, take a few moments to carefully examine the graph and identify the key trends, patterns, and significant features.
Ask yourself these questions:
- What is the general trend shown in the graph?
- Are there any notable increases or decreases?
- Do any periods of stability or fluctuation stand out?
- What are the highest and lowest points on the graph?
2. Structure Your Response Effectively
A well-organized response is crucial for clarity and coherence. Use a logical structure to present your analysis. A typical structure for a line graph report includes:
-
Introduction (Paragraph 1):
- Paraphrase the question prompt, providing an overview of the graph’s subject and time period.
- Example: “The line graph illustrates the changes in the average price of gasoline in the United States between 2000 and 2020.”
-
Overview (Paragraph 2):
- Summarize the most significant trends, patterns, or changes depicted in the graph. This provides a general understanding of the data without going into specific details.
- Example: “Overall, the graph reveals a fluctuating trend in gasoline prices over the two decades, with a noticeable surge in prices after 2005.”
-
Body Paragraphs (Paragraph 3 onwards):
- Describe the key features in detail, supporting your statements with data from the graph.
- Organize your body paragraphs logically, grouping similar trends or patterns together.
- Use specific data points to support your observations, highlighting significant increases, decreases, or fluctuations.
- Example: “From 2000 to 2005, gasoline prices remained relatively stable, hovering around $1.50 per gallon. However, after 2005, prices experienced a sharp increase, reaching a peak of $4.00 per gallon in 2008.”
-
Conclusion (Optional):
- Briefly summarize the main trends or patterns discussed in the body paragraphs.
- You can omit the conclusion if you’ve already summarized the key findings in your overview paragraph.
3. Use Precise Language and Vocabulary
Employ a wide range of vocabulary to describe trends, changes, and comparisons. Avoid repeating the same words or phrases.
Verbs to Describe Trends:
- Increase: rise, climb, surge, soar, escalate, grow
- Decrease: decline, fall, drop, plummet, dwindle, decrease
- Fluctuate: oscillate, vary, change, shift, alter
- Remain stable: stabilize, level off, remain constant
Adverbs to Indicate Degree of Change:
- Sharply: dramatically, significantly, substantially
- Gradually: steadily, progressively, moderately
- Slightly: marginally, minimally
Prepositions for Time and Comparisons:
- From (start point) to (end point)
- Between (time period) and (time period)
- Over a period of (duration)
- Compared to
- In contrast to
4. Support Your Statements with Data
Whenever you mention a trend or pattern, make sure to support it with specific data from the graph. This demonstrates your ability to interpret and present data accurately.
- Example: “The number of students enrolled in online courses increased dramatically from 10,000 in 2010 to 50,000 in 2020.”
5. Proofread for Grammar and Vocabulary Errors
Before submitting your response, carefully proofread your work for any grammatical or vocabulary errors. Pay close attention to subject-verb agreement, tense consistency, and word choice.
Example Line Graph Report
Question:
The line graph below shows the number of tourists visiting a particular country over a 12-month period.
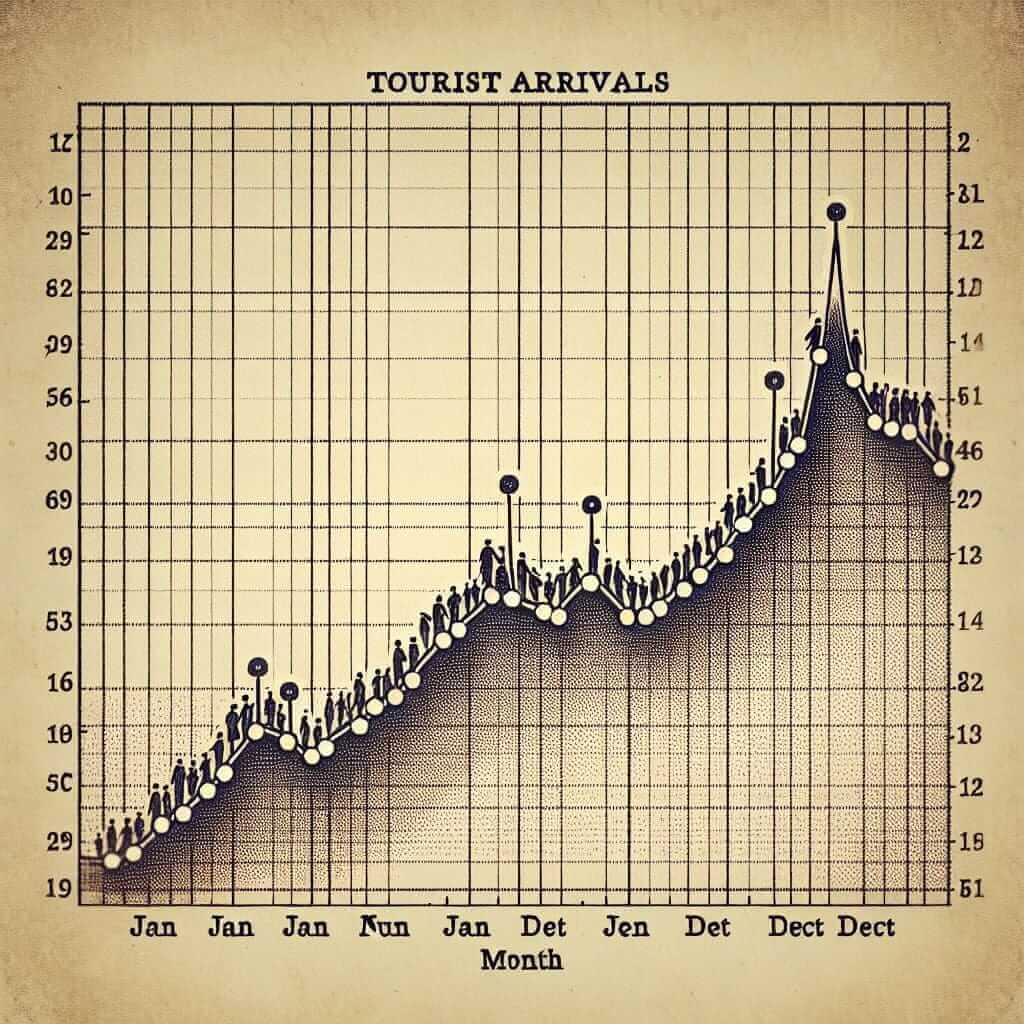
Summarize the information by selecting and reporting the main features and make comparisons where relevant.
Answer:
The line graph illustrates the monthly fluctuations in tourist arrivals to a specific country over the course of a year.
Overall, the graph reveals a cyclical pattern in tourist numbers, with a peak season during the summer months and a decline during the winter months.
From January to April, tourist arrivals show a steady upward trend, increasing from 10,000 to 30,000. This is followed by a sharp surge in May and June, with numbers peaking at 50,000 in June, coinciding with the start of the summer season.
However, tourist numbers experience a steep decline from July to September, falling to 20,000 by September. This downward trend continues, albeit at a slower pace, throughout the autumn months, reaching a low of 10,000 in December.
Tips for Achieving a Band 9 in IELTS Writing Task 1
- Practice Regularly: Practice writing line graph reports using past IELTS exam questions or sample tasks. This will help you familiarize yourself with the task format and improve your timing.
- Focus on Coherence and Cohesion: Use linking words and phrases to ensure a smooth flow of ideas between sentences and paragraphs. This enhances the overall coherence of your writing.
- Vary Your Sentence Structure: Avoid using repetitive sentence structures. Incorporate a mix of simple, compound, and complex sentences to add variety and sophistication to your writing.
- Pay Attention to Spelling and Punctuation: Errors in spelling and punctuation can lower your score. Proofread carefully to eliminate these mistakes.
- Seek Feedback: Ask a teacher, tutor, or fluent English speaker to review your writing and provide feedback on areas for improvement.
By following these tips and practicing consistently, you can develop the necessary skills and confidence to excel in the IELTS Writing Task 1 line graph description. Good luck!