As an IELTS instructor with over 20 years of experience, I’ve witnessed countless students grapple with the speaking section. Many struggle to articulate their thoughts effectively, often feeling their English fluency falters under pressure. The key to unlocking confident and articulate communication lies in understanding how our brains process language, especially in a high-stakes environment like the IELTS.
The Relevance of Language Processing to IELTS Speaking
Knowing how your brain tackles language, from comprehension to production, offers invaluable insights for IELTS preparation. This understanding helps you:
- Optimize learning strategies: By adapting your study methods to your brain’s natural language acquisition processes, you can learn vocabulary and grammar structures more efficiently.
- Improve fluency and coherence: Recognizing the stages of language production allows you to identify and address potential roadblocks, leading to smoother and more coherent speech.
- Boost confidence: Understanding the science behind language processing can demystify the speaking exam, replacing anxiety with a sense of control and preparedness.
How Our Brains Decode and Produce Language
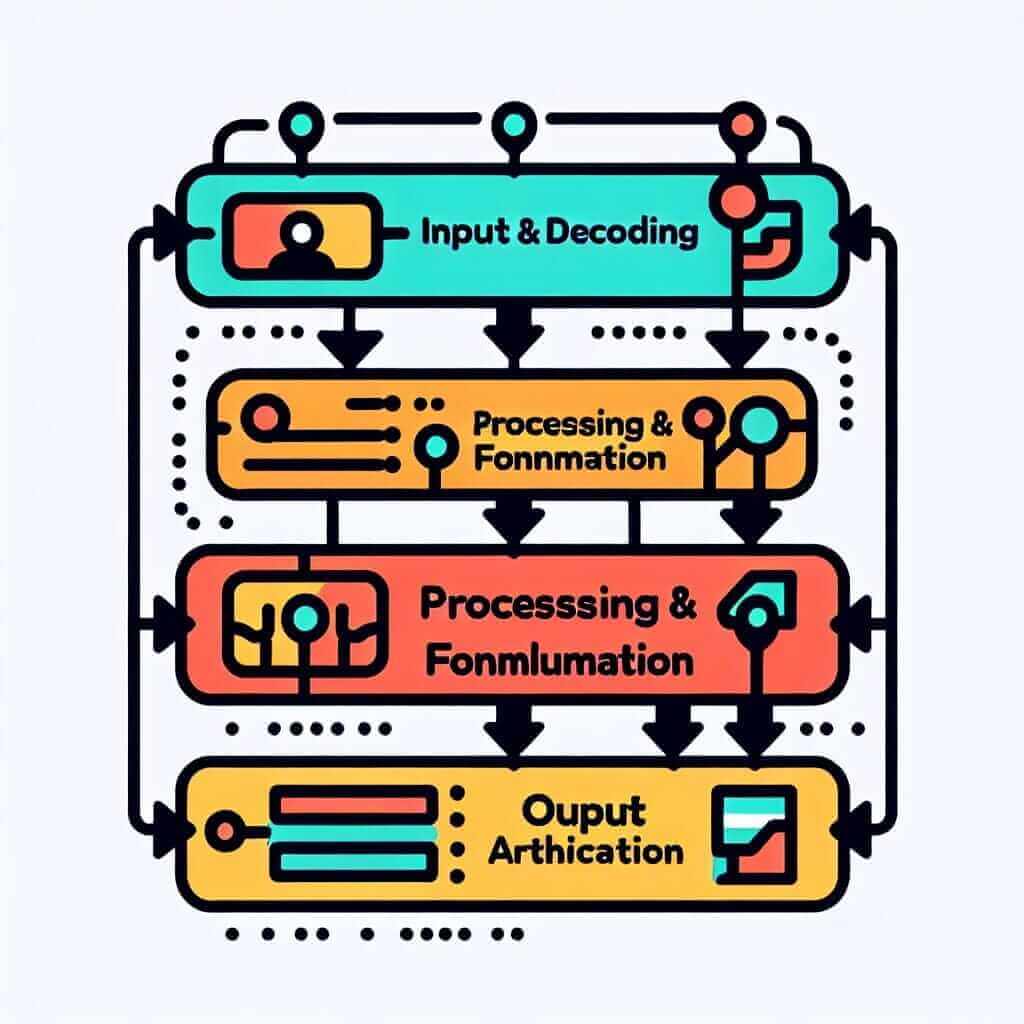
While the intricacies of language processing are complex, a simplified model can be incredibly helpful for IELTS preparation. Let’s break down the process:
1. Input and Decoding:
This stage involves receiving auditory or visual language input. Your brain works rapidly to:
- Recognize sounds and patterns: Distinguish individual sounds (phonemes) and identify patterns to recognize words.
- Access meaning: Retrieve word definitions and grammatical rules from your mental lexicon.
- Interpret context: Analyze the overall message by connecting words, sentences, and paragraphs.
2. Processing and Formulation:
Here, your brain springs into action to formulate a response:
- Idea generation: Activate relevant knowledge and formulate thoughts based on the input.
- Grammatical structuring: Organize ideas into grammatically correct sentences, applying appropriate tenses and structures.
- Lexical selection: Choose the most accurate and expressive vocabulary to convey your message.
3. Output and Articulation:
Finally, your brain translates thoughts into spoken words:
- Motor planning: Signals are sent to your muscles controlling speech production (tongue, lips, vocal cords).
- Sound articulation: Produce a sequence of sounds to form words and sentences.
- Self-monitoring: Simultaneously listen to your own speech, making adjustments for clarity and fluency.
Applying this Knowledge to the IELTS Speaking Test
Let’s look at a sample IELTS Speaking Part 3 question:
“Some people believe that learning a foreign language changes our view of the world. What is your opinion?”
Using your understanding of language processing:
- Decoding: You quickly identify keywords like “foreign language,” “changes,” “view of the world,” and “opinion” to grasp the question’s essence.
- Processing: You access your knowledge about language learning and its potential impact on perspectives, formulating a coherent stance.
- Articulation: You structure your response using appropriate vocabulary and grammar, aiming for clarity and a natural flow of speech.
Tips for Maximizing Your Language Processing Abilities
- Active Listening: Engage in conversations, watch movies, and listen to podcasts to train your brain in decoding and processing English.
- Vocabulary Expansion: Regularly learn new words and practice using them in context to strengthen your lexical retrieval.
- Grammar Focus: Dedicate time to understanding and practicing various grammatical structures, enabling smoother sentence construction.
- Speak Aloud: Regularly practice speaking English, even if it’s to yourself, to enhance articulation and fluency.
- Mock Tests: Simulate exam conditions with timed mock tests to familiarize yourself with the pressure and refine your language processing under stress.
Conclusion
Mastering the IELTS Speaking test demands more than just memorizing vocabulary and grammar rules. It requires a deeper understanding of how your brain processes language. By working with your natural cognitive abilities and employing effective practice strategies, you can unlock confident and articulate communication, paving your path to IELTS success.