The IELTS Reading test can be challenging, especially when it comes to unfamiliar topics. Today, we’ll explore a practice test focused on AI-powered tools for language instruction, a cutting-edge area in education technology. This test will help you hone your skills while learning about an exciting field that’s reshaping language education.
Passage 1 (Easy Text)
The Rise of AI in Language Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing many aspects of our lives, and language learning is no exception. In recent years, AI-powered tools have become increasingly sophisticated, offering personalized learning experiences that were once unimaginable. These tools can adapt to individual learning styles, provide instant feedback, and even simulate real-life conversations.
One of the most significant advantages of AI in language learning is its ability to analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and trends in language usage. This allows AI systems to offer tailored recommendations and exercises based on a learner’s specific needs and progress. For example, if a student consistently struggles with certain grammatical structures, the AI can generate targeted practice exercises to address these weaknesses.
Moreover, AI-powered language learning platforms can provide learners with immersive experiences through virtual and augmented reality technologies. These innovations allow students to practice their language skills in simulated real-world environments, enhancing their ability to apply what they’ve learned in practical situations.
As AI-powered educational tools continue to evolve, they are becoming increasingly integrated into traditional language instruction methods. Many language schools and educational institutions now use AI-powered platforms to complement their curricula, providing students with additional resources and practice opportunities outside the classroom.
Questions 1-5
Do the following statements agree with the information given in the passage? Write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
- AI-powered tools can adapt to individual learning styles.
- AI systems can only provide feedback on written language skills.
- AI-powered platforms use virtual reality to create immersive learning experiences.
- Traditional language schools are completely replacing their curricula with AI tools.
- AI can analyze language usage patterns to offer personalized recommendations.
Questions 6-10
Complete the sentences below. Choose NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from the passage for each answer.
- AI-powered tools offer __ learning experiences that were previously not possible.
- AI systems can generate __ exercises to address specific weaknesses in language learning.
- Virtual and augmented reality technologies provide learners with __ experiences.
- AI-powered platforms are becoming increasingly __ into traditional language instruction methods.
- Many educational institutions use AI tools to __ their existing curricula.
Passage 2 (Medium Text)
The Impact of AI on Language Instruction Methodologies
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into language instruction has sparked a paradigm shift in teaching methodologies. Traditional approaches to language education are being augmented and, in some cases, transformed by the capabilities of AI-powered tools. This evolution is not only changing how languages are taught but also how they are learned and practiced.
One of the most significant impacts of AI on language instruction is the enhancement of personalized learning. AI algorithms can analyze a learner’s performance, identify areas of weakness, and create custom learning paths. This level of individualization was previously impossible for human teachers to achieve consistently across large groups of students. Now, each learner can progress at their own pace, focusing on areas that require the most attention.
Moreover, AI has revolutionized the concept of immediate feedback in language learning. While human teachers can provide feedback during class time or on assignments, AI-powered tools offer instant corrections and explanations 24/7. This constant availability of feedback accelerates the learning process and allows students to make corrections in real-time, reinforcing proper language usage.
Another area where AI is making significant strides is in speech recognition and pronunciation training. Advanced AI systems can now detect subtle nuances in pronunciation, offering learners precise feedback on their speaking skills. This technology enables students to practice speaking without the fear of judgment, encouraging more frequent oral practice and ultimately leading to improved fluency.
The implementation of AI in language instruction has also led to the development of more engaging and interactive learning materials. AI can generate dynamic content that adapts to the learner’s interests and proficiency level, making the learning process more enjoyable and relevant. For instance, an AI system might create personalized reading materials based on a student’s hobbies or career aspirations, increasing motivation and retention.
Furthermore, AI is facilitating the preservation of ancient languages and dialects. By analyzing vast corpora of text and audio data, AI can help reconstruct languages with limited native speakers, providing valuable resources for linguists and preserving cultural heritage.
However, the integration of AI in language instruction is not without challenges. There are concerns about data privacy, the potential for AI to reinforce biases present in training data, and the risk of over-reliance on technology at the expense of human interaction. Educators and policymakers must navigate these issues carefully to ensure that AI enhances rather than diminishes the quality of language education.
As we look to the future, it’s clear that AI will continue to play an increasingly important role in language instruction. The key will be to find the right balance between AI-powered tools and human expertise, leveraging the strengths of both to create more effective and accessible language learning experiences for students worldwide.
Questions 11-15
Choose the correct letter, A, B, C, or D.
-
According to the passage, how has AI changed personalized learning in language instruction?
A) By replacing human teachers entirely
B) By allowing students to design their own curricula
C) By creating custom learning paths based on individual performance
D) By focusing only on advanced learners -
What advantage does AI-powered feedback have over traditional feedback methods?
A) It is more accurate than human feedback
B) It is available at all times
C) It only focuses on grammar corrections
D) It eliminates the need for human teachers -
How does AI contribute to speech recognition and pronunciation training?
A) By replacing human conversation partners
B) By detecting subtle differences in pronunciation
C) By teaching only standard accents
D) By eliminating the need for oral practice -
What is mentioned as a potential challenge of integrating AI in language instruction?
A) The high cost of implementation
B) The lack of engaging content
C) The risk of over-reliance on technology
D) The inability to teach advanced language skills -
According to the passage, what is the key to successfully integrating AI in language education?
A) Completely replacing human teachers with AI
B) Using AI only for beginner-level instruction
C) Finding a balance between AI tools and human expertise
D) Focusing solely on pronunciation training
Questions 16-20
Complete the summary below. Choose NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from the passage for each answer.
AI is revolutionizing language instruction by offering personalized learning experiences and (16) __ feedback. It excels in areas such as speech recognition and pronunciation training, allowing students to practice without (17) __ . AI also creates (18) __ learning materials that adapt to learners’ interests. Additionally, AI is helping to (19) __ ancient languages by analyzing large amounts of data. However, there are concerns about issues such as data privacy and potential (20) __ in AI systems, which need to be carefully addressed.
Passage 3 (Hard Text)
The Cognitive Implications of AI-Assisted Language Acquisition
The advent of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in language learning has not only revolutionized pedagogical approaches but also prompted a reevaluation of the cognitive processes involved in second language acquisition. As AI-powered tools become increasingly sophisticated, researchers are examining how these technologies interact with and potentially reshape the neural pathways associated with language learning.
One of the most intriguing areas of study is the impact of AI-assisted learning on neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to form and reorganize synaptic connections in response to learning or experience. Traditional language learning methods have been shown to enhance neuroplasticity, particularly in regions associated with language processing such as Broca’s and Wernicke’s areas. However, the constant, personalized feedback and adaptive learning provided by AI tools may accelerate and intensify these neuroplastic changes.
Recent neuroimaging studies have suggested that learners using AI-powered language tools exhibit increased activation in the prefrontal cortex, an area associated with executive functions such as decision-making and problem-solving. This heightened activity may be attributed to the gamification elements often incorporated into AI learning platforms, which require learners to make quick decisions and strategize their learning approach.
Moreover, the ability of AI systems to provide instant feedback and correction may be altering the way learners process and internalize linguistic information. The error correction process, traditionally mediated by human instructors over extended periods, is now compressed into rapid, iterative cycles. This acceleration could potentially lead to faster acquisition of correct language patterns, but it also raises questions about the depth and durability of the learning.
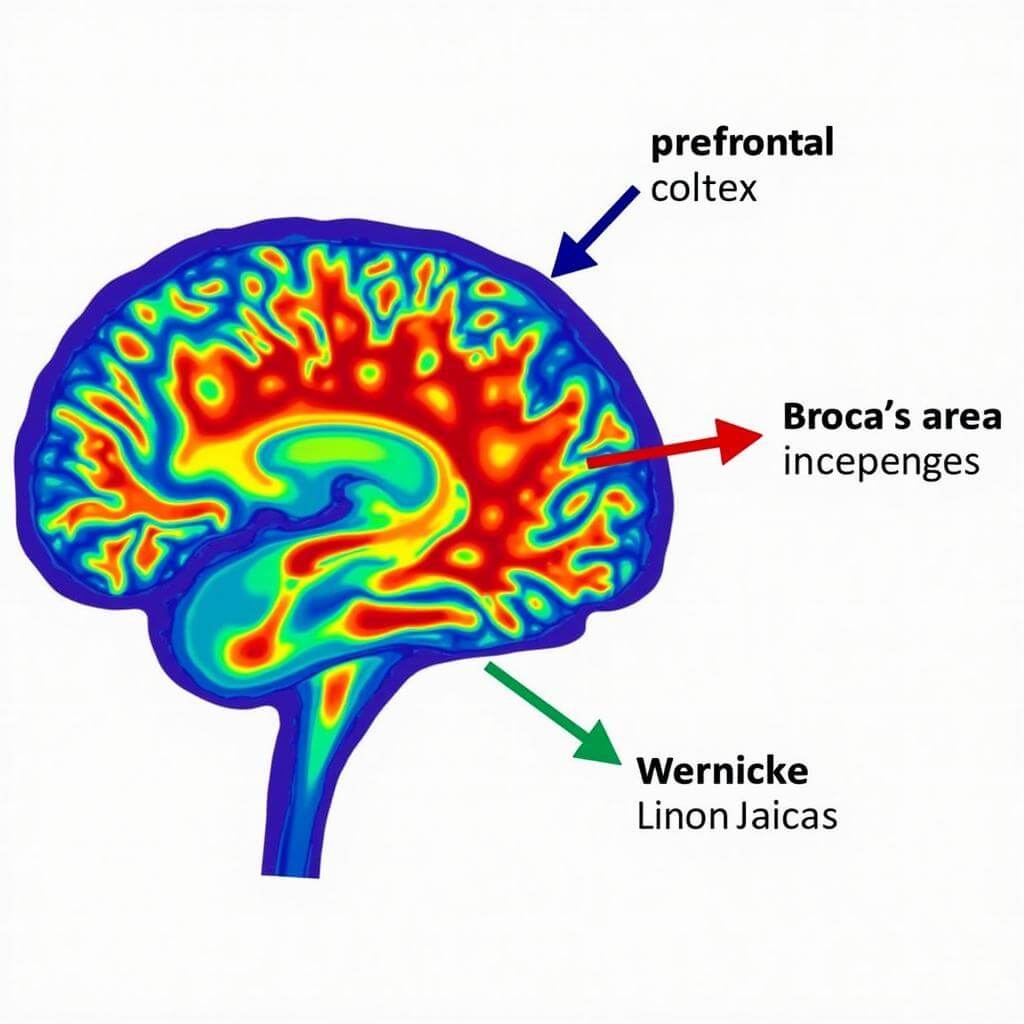
Another significant cognitive implication of AI in language learning is its potential to enhance metalinguistic awareness – the ability to reflect on and manipulate the structural features of language. AI tools often provide detailed explanations of grammar rules and linguistic patterns, encouraging learners to think analytically about language. This explicit focus on language structures may foster a deeper understanding of the target language and potentially facilitate transfer to other languages.
The multimodal nature of many AI language learning platforms, which often integrate text, audio, and visual elements, aligns well with theories of multiple intelligences and learning styles. By engaging multiple sensory channels simultaneously, these tools may enhance memory consolidation and recall, potentially leading to more robust language acquisition.
However, the reliance on AI for language learning is not without potential drawbacks from a cognitive perspective. There are concerns that the convenience and immediacy of AI-assisted learning might lead to a reduction in cognitive effort, potentially undermining the deep processing necessary for long-term retention. The concept of “desirable difficulties” in learning suggests that some level of struggle is beneficial for robust learning outcomes.
Furthermore, the highly structured and predictable nature of AI learning environments may not adequately prepare learners for the ambiguity and contextual nuances inherent in real-world language use. The spontaneity and unpredictability of human conversation, with its myriad social and cultural cues, remain challenging to replicate fully in AI systems.
As AI continues to evolve, it is likely to have an increasingly profound impact on the cognitive aspects of language acquisition. While it offers unprecedented opportunities for personalized, efficient learning, it also necessitates a careful consideration of how to balance technological assistance with the cognitive challenges essential for deep, lasting language proficiency. Artificial intelligence is improving language instruction in many ways, but it’s crucial to understand its cognitive implications to harness its full potential.
The future of AI in language learning will likely involve a symbiotic relationship between technology and human cognition, where AI tools are designed not just to facilitate learning, but to optimally engage and enhance the brain’s natural language acquisition processes. As our understanding of both AI and cognitive science deepens, we can expect to see increasingly sophisticated and neuroscientifically informed approaches to AI-assisted language instruction.
Questions 21-26
Complete the summary below. Choose NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from the passage for each answer.
AI-powered language learning tools are changing the way we think about cognitive processes in language acquisition. These tools may enhance (21) __, particularly in brain regions associated with language processing. Studies have shown increased activity in the (22) __, which is linked to executive functions. The rapid feedback provided by AI systems could alter how learners (23) __ linguistic information. AI tools may also improve (24) __, the ability to analyze language structures. However, there are concerns that AI-assisted learning might reduce (25) __, which is important for deep learning. The structured nature of AI environments may not fully prepare learners for the (26) __ of real-world language use.
Questions 27-31
Choose FIVE letters, A-H.
Which FIVE of the following are mentioned in the passage as aspects or effects of AI-assisted language learning?
A) Enhanced neuroplasticity in language-related brain areas
B) Decreased activity in the prefrontal cortex
C) Rapid cycles of error correction and feedback
D) Reduced need for human language instructors
E) Improved metalinguistic awareness
F) Engagement of multiple sensory channels in learning
G) Guaranteed long-term retention of language skills
H) Potential reduction in cognitive effort during learning
Questions 32-35
Do the following statements agree with the claims of the writer in the passage? Write
YES if the statement agrees with the claims of the writer
NO if the statement contradicts the claims of the writer
NOT GIVEN if it is impossible to say what the writer thinks about this
- AI-powered language learning tools always lead to better learning outcomes than traditional methods.
- The gamification elements in AI platforms may contribute to increased prefrontal cortex activity.
- AI-assisted language learning can potentially enhance transfer of skills between languages.
- The future of language learning will completely eliminate the need for human instructors.
Questions 36-40
Complete the sentences below. Choose NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from the passage for each answer.
- The concept of __ suggests that some level of struggle is beneficial for robust learning outcomes.
- AI tools often provide detailed explanations of __ and linguistic patterns.
- The __ of human conversation, with its various social and cultural cues, is difficult to fully replicate in AI systems.
- Future AI tools may be designed to optimally engage and enhance the brain’s natural __ processes.
- The integration of AI in language learning necessitates a balance between technological assistance and __ essential for deep language proficiency.
Answer Key
Passage 1
- TRUE
- NOT GIVEN
- TRUE
- FALSE
- TRUE
- personalized
- targeted
- immersive
- integrated
- complement
Passage 2
- C
- B
- B
- C
- C
- immediate
- fear of judgment
- engaging and interactive
- preserve
- biases
Passage 3
- neuroplasticity
- prefrontal cortex
- process and internalize
- metalinguistic awareness
- cognitive effort
- ambiguity / unpredictability
- A, C, E, F, H
- YES
- YES
- NOT GIVEN
- NO
- desirable difficulties
- grammar rules
- spontaneity
- language acquisition
- cognitive challenges
By practicing with these AI-themed IELTS Reading passages, you’re not only preparing for your test but also gaining insights into how AI-powered educational tools are shaping the future of language learning. Remember to apply critical reading skills and time management strategies as you work through these questions. Good luck with your IELTS preparation!