Healthcare spending is a critical aspect of a country’s development, impacting both the well-being of its citizens and the efficiency of its economy. In the context of the IELTS Writing Task 1, analyzing and comparing the levels of healthcare spending in different regions over a period can provide a comprehensive overview and enhance the analytical skills required for achieving a high band score. This article will delve into the trends, vocabulary, and grammatical structures pertinent to this task.
To illustrate, let’s consider the following IELTS Writing Task 1 prompt:
Task 1 Prompt:
The bar chart below shows the healthcare spending in different regions from 2000 to 2023.
Analyzing the Task
To handle this task effectively:
- Identify the main trends: Look for significant increases, decreases, and patterns.
- Compare and contrast: Discuss similarities and differences between regions.
- Summarize key points: Conclude by summarizing the main findings without adding personal opinions or new information.
Data Presentation
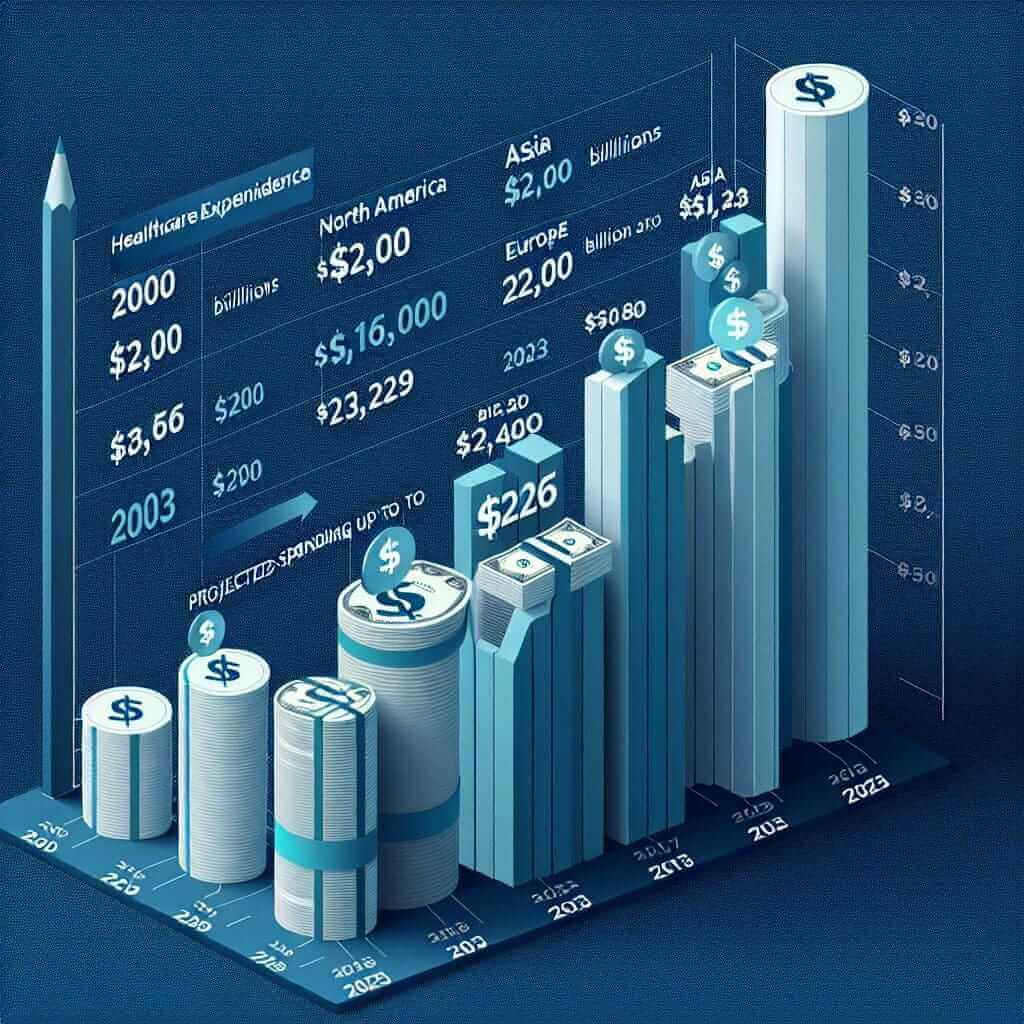
Here is an example bar chart illustrating healthcare spending in North America, Europe, and Asia from 2000 to 2023.
Model Answer
Let’s draft a model answer for the above task.
Healthcare Spending in Different Regions (2000-2023)
The bar chart illustrates the amount of spending on healthcare in North America, Europe, and Asia from 2000 to 2023.
Overall, it is evident that healthcare expenditure has increased in all regions over the given period. However, North America consistently spends a significantly higher amount compared to Europe and Asia.
In 2000, North America’s spending was approximately $500 billion, which then escalated to around $700 billion in 2023. Europe started with a much lower figure of $300 billion in 2000, eventually reaching $450 billion by 2023. Asia, while the least in spending, saw an increase from $200 billion in 2000 to close to $350 billion in 2023.
Asia exhibited the most significant growth rate, almost doubling its expenditure over the 23 years. Europe’s spending also showed a steady rise, albeit at a slower rate compared to Asia. Despite the continuous increase in expenditure in all three regions, North America remains the highest spender on healthcare, followed by Europe and then Asia.
Word Count: 177
Key Vocabulary and Phrases
- Escalated (verb) /ˈɛskəˌleɪtɪd/: to increase rapidly.
- Example: The healthcare spending escalated from $500 billion to $700 billion.
- Expenditure (noun) /ɪkˈspɛndɪtʃər/: the action of spending funds.
- Example: The expenditure on healthcare in North America is the highest.
- Significantly (adverb) /sɪɡˈnɪfɪkəntli/: in a way that is large or important enough to be noticed or have an effect.
- Example: Spending has increased significantly over the period.
- Consistently (adverb) /kənˈsɪstəntli/: in every case or on every occasion; invariably.
- Example: North America consistently spends more on healthcare.
- Exhibit (verb) /ɪɡˈzɪbɪt/: to show an amount, quality, or some feature.
- Example: Asia exhibited the most significant growth rate.
Grammatical Structures to Use
-
Comparative and Superlative Adjectives:
- Example: North America’s spending is higher than that of Europe and Asia (comparative).
- Example: North America is the highest spender on healthcare (superlative).
-
Passive Voice:
- Example: The healthcare expenditure in these regions has been increased over the years.
-
Time Phrases:
- Example: Throughout the period from 2000 to 2023, spending has risen significantly.
- Example: In 2000, the expenditure was only $200 billion.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when tackling a task on comparing levels of healthcare spending in different regions, it is crucial to highlight the key trends, make clear comparisons, and provide a concise summary. Utilizing the appropriate vocabulary, sticking to the structure, and ensuring grammatical accuracy are essential steps to achieving a Band 7+ in the IELTS Writing Task 1.
By practicing such tasks, candidates can hone their analytical writing skills and be better prepared for the IELTS exam.