The topic of Cultural Heritage Sites Visitors frequently surfaces in IELTS Writing Task 1, demanding test-takers to analyze and articulate trends based on presented data. This article will delve into this topic, providing a comprehensive guide to help you excel in this IELTS section. We will analyze real data, craft a band-worthy response, and highlight key vocabulary and grammar points crucial for a high score.
Sample IELTS Writing Task 1 Question
Let’s imagine you are presented with the following IELTS Writing Task 1 question:
The chart below shows the number of visitors to five different cultural heritage sites in a European country between 2000 and 2020.
Summarize the information by selecting and reporting the main features and making comparisons where relevant.
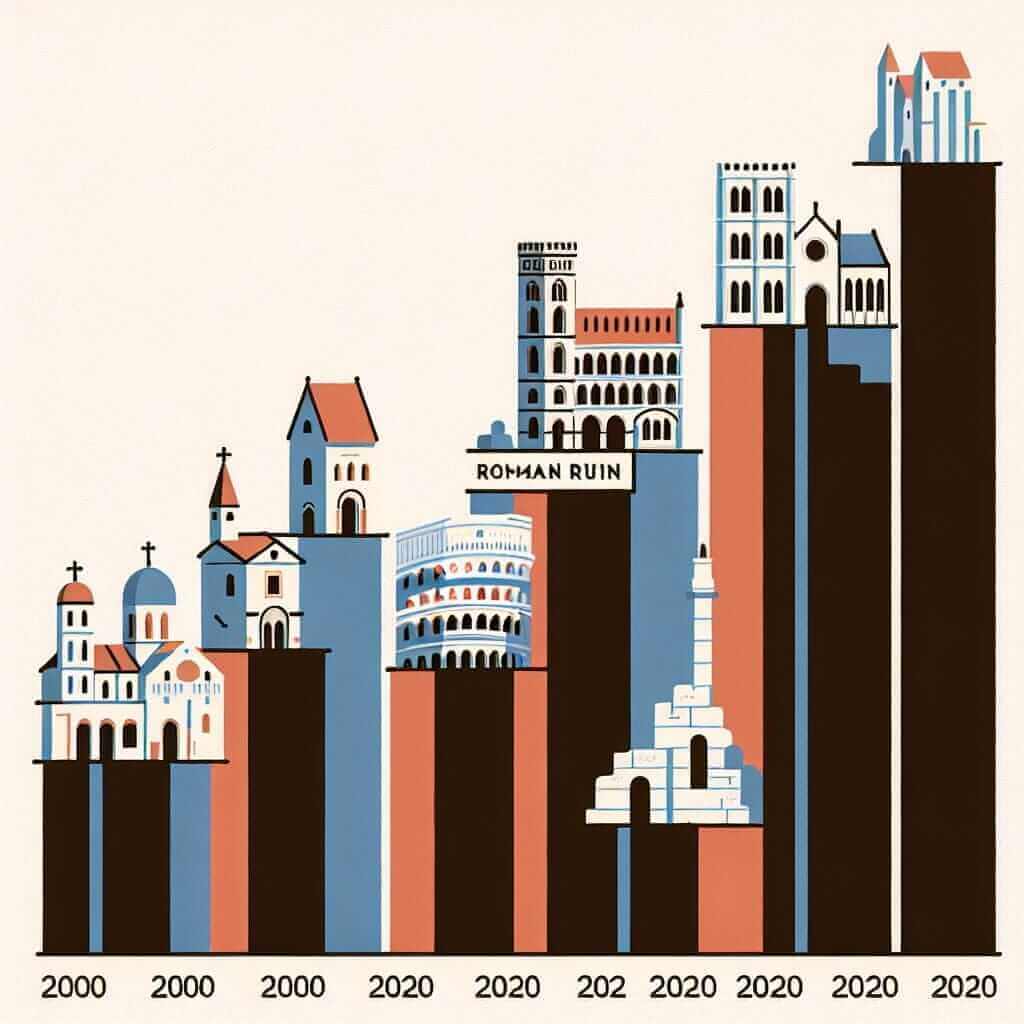
(Insert a bar chart here with data on visitor numbers for five cultural heritage sites: a castle, a Roman ruin, a historic town, a cathedral, and a museum, spanning from 2000 to 2020. Show varying trends for each site, like increasing, decreasing, or fluctuating numbers).
Data Analysis and Writing a Band 7+ Response
Analyzing the Task
Before diving into writing, let’s break down the task:
- Type of chart: Bar chart
- Time period: 20 years (2000-2020)
- Key information: Visitor numbers to five different cultural heritage sites
- Task: Summarize key trends, make comparisons
Model Answer
The bar chart illustrates the visitor figures for five distinct cultural heritage sites in a European nation over a twenty-year period, from 2000 to 2020.
Overall, the castle consistently attracted the highest number of visitors throughout the period, while the museum experienced the most significant growth in popularity.
In 2000, the castle welcomed approximately 800,000 visitors, considerably more than the other sites. The Roman ruin and the historic town had similar visitor numbers, around 400,000 and 350,000 respectively. The cathedral attracted a modest 200,000 visitors, while the museum saw the lowest number at a mere 100,000.
Over the two decades, the castle witnessed a gradual increase in visitor numbers, reaching a peak of just over 1 million in 2020. Interestingly, the museum exhibited a dramatic surge in popularity, with visitor figures skyrocketing from 100,000 in 2000 to nearly 700,000 in 2020. The historic town also experienced a steady rise in visitors, reaching approximately 600,000 by 2020.
Conversely, both the Roman ruin and the cathedral saw relatively stable visitor numbers, hovering around their initial figures throughout the period.
(Word count: 180 words)
Key Points and Vocabulary
Structure:
- Introduction: Paraphrasing the question and providing an overview.
- Overview: Highlighting the most striking trends.
- Body paragraphs: Describing specific details and making comparisons.
Vocabulary:
- Visitors: Tourists, attendees
- Cultural heritage sites: Historical landmarks, ancient monuments
- Consistently: Steadily, invariably
- Growth in popularity: Increased interest, rising demand
- Dramatic surge: Sharp increase, rapid growth
- Skyrocketing: Increasing dramatically, soaring
- Steady rise: Gradual increase, continuous growth
- Relatively stable: Constant, unchanging
Grammar:
- Use of past tense to describe past events.
- Use of comparatives and superlatives to make comparisons.
- Use of adverbs to describe the degree or manner of change.
Essential Vocabulary for Cultural Heritage Sites
Here are some additional words and phrases to boost your vocabulary for this topic:
- Preservation (n.) /prɪzəˈveɪʃən/: The act of keeping something in its original state or protecting it from damage.
- Restoration (n.) /ˌrɛstəˈreɪʃən/: The process of repairing and cleaning a building or work of art to return it to its original condition.
- Conservation (n.) /ˌkɒnsəˈveɪʃən/: The protection of plants, animals, and natural areas, especially from the damaging effects of human activity.
- World Heritage Site (n.) /wɜːld ˈhɛrɪtɪdʒ saɪt/: A place (such as a building, city, forest, or island) that has special cultural or physical significance and is protected by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO).
- Tourist attraction (n.) /ˈtʊərɪst əˈtrækʃən/: A place that tourists visit for its historical significance, natural beauty, or entertainment value.
- Archaeological site (n.) /ˌɑːkiəˈlɒdʒɪkəl saɪt/: A place where archaeologists study past human activity by excavating and examining material remains.
Conclusion
Mastering the IELTS Writing Task 1 requires a combination of analytical skills, vocabulary, and grammatical accuracy. By understanding data trends, utilizing appropriate vocabulary, and structuring your response coherently, you can achieve a high score in this section. Remember to practice regularly with various charts and data sets to gain confidence and improve your writing proficiency.