The IELTS Reading test assesses your ability to comprehend complex texts on a variety of topics. Today, we’ll focus on “Global Partnerships in Higher Education,” a subject that frequently appears in IELTS exams. Let’s explore this theme through a complete IELTS Reading practice test.
How online learning is transforming rural education has paved the way for global partnerships in higher education. These collaborations are now extending beyond traditional boundaries, creating new opportunities for students worldwide.
Practice Test: Global Partnerships in Higher Education
Passage 1 – Easy Text
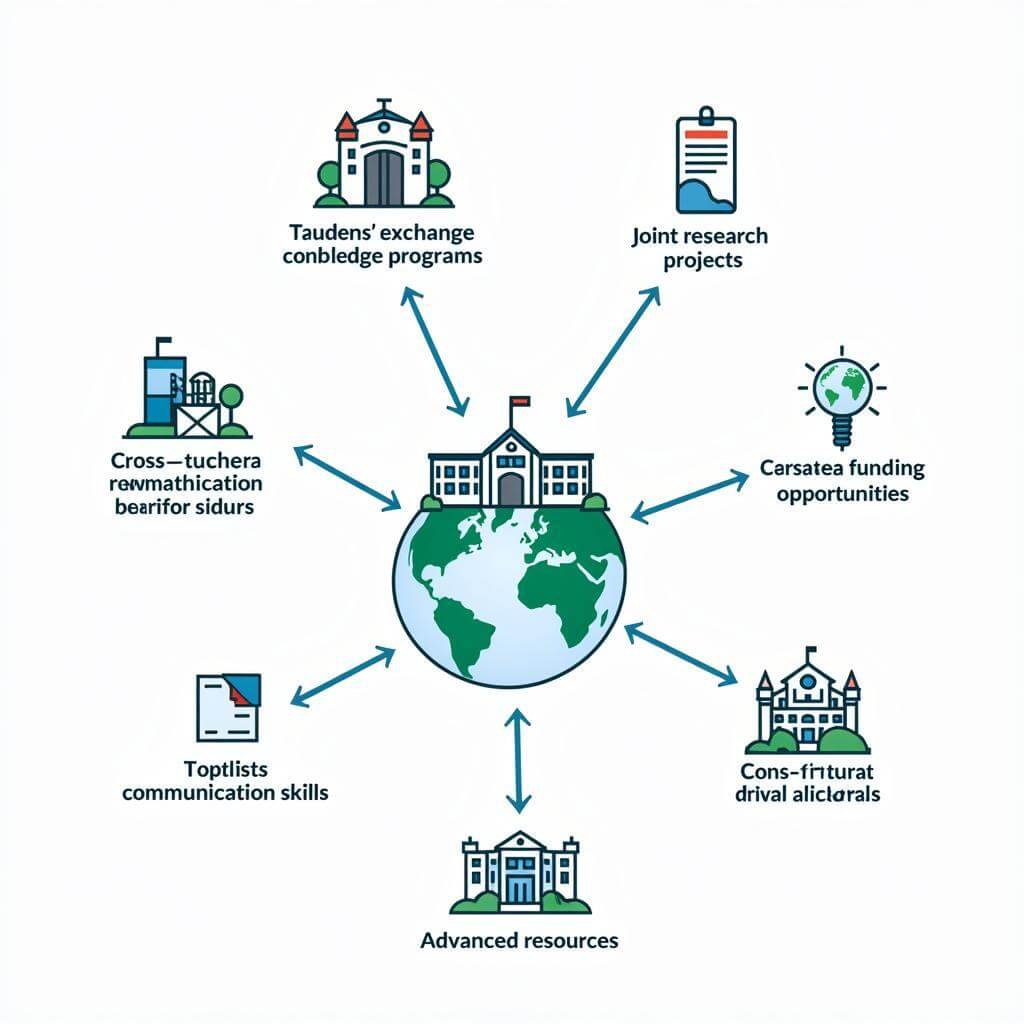
International cooperation in higher education has become increasingly important in today’s globalized world. Universities across the globe are forming partnerships to enhance research, improve teaching methods, and provide students with diverse learning experiences. These collaborations often involve student exchange programs, joint research projects, and shared curriculum development.
One of the primary benefits of global partnerships is the exposure students gain to different cultures and perspectives. By studying abroad or participating in international projects, students develop cross-cultural communication skills and global awareness, which are highly valued in the modern workforce. Additionally, these partnerships often lead to increased funding opportunities and access to advanced resources that may not be available at a single institution.
However, establishing and maintaining successful global partnerships is not without challenges. Language barriers, differences in academic standards, and varying cultural norms can complicate collaboration efforts. Universities must navigate these obstacles carefully to ensure that partnerships are mutually beneficial and sustainable in the long term.
Despite these challenges, the trend towards global partnerships in higher education continues to grow. Many institutions now consider international collaboration a key component of their strategic plans, recognizing its potential to enhance their reputation and attract top talent from around the world.
Questions 1-5
Choose the correct letter, A, B, C, or D.
-
What is one of the main advantages of global partnerships in higher education?
A) Reduced tuition fees
B) Guaranteed job placements
C) Exposure to different cultures
D) Simplified visa processes -
According to the passage, what skill do students develop through international experiences?
A) Technical expertise
B) Cross-cultural communication
C) Athletic abilities
D) Political acumen -
Which of the following is NOT mentioned as a challenge in establishing global partnerships?
A) Language barriers
B) Differences in academic standards
C) Financial constraints
D) Varying cultural norms -
How do many institutions view international collaboration?
A) As an unnecessary expense
B) As a temporary trend
C) As a key component of strategic plans
D) As a minor aspect of education -
What potential benefit of global partnerships for universities is mentioned in the passage?
A) Increased student enrollment
B) Enhanced reputation
C) Lower operating costs
D) Simplified accreditation processes
Passage 2 – Medium Text
The landscape of higher education is rapidly evolving, with global partnerships playing an increasingly pivotal role in shaping the future of academic institutions worldwide. These collaborations are not merely about exchanging students or faculty; they represent a fundamental shift in how universities approach education, research, and innovation in an interconnected world.
One of the most significant impacts of global partnerships is on research output and quality. When institutions from different countries collaborate, they bring together diverse perspectives, methodologies, and resources. This synergy often leads to groundbreaking discoveries and innovations that might not have been possible within the confines of a single institution or national context. For instance, international research teams are at the forefront of addressing global challenges such as climate change, public health crises, and technological advancements.
Moreover, these partnerships are instrumental in fostering academic mobility. Students and faculty members who participate in exchange programs or joint degree offerings gain invaluable international experience. This exposure not only enhances their personal and professional development but also contributes to the creation of a global workforce equipped to navigate the complexities of an increasingly interconnected world economy.
The rise of virtual mentoring in global education has further amplified the reach and impact of these partnerships. Digital platforms now enable real-time collaboration between students and faculty across continents, breaking down geographical barriers and democratizing access to global educational resources.
However, the implementation of global partnerships is not without its challenges. Disparities in funding, differences in academic calendars, and varying quality assurance standards can create obstacles in establishing and maintaining these collaborations. Additionally, there are concerns about brain drain from developing countries, as talented individuals may choose to remain in more developed nations after their educational experiences abroad.
To address these challenges, many institutions are adopting innovative approaches. Some are creating regional hubs or satellite campuses in partner countries, allowing for a more balanced exchange of knowledge and resources. Others are focusing on capacity-building initiatives that aim to strengthen the educational infrastructure in developing nations, ensuring that partnerships are truly mutually beneficial.
The future of global partnerships in higher education looks promising, with emerging technologies opening up new avenues for collaboration. Virtual reality and augmented reality tools are beginning to offer immersive international experiences without the need for physical travel, potentially making global education more accessible and sustainable.
As these partnerships continue to evolve, they are likely to play a crucial role in addressing global skills gaps, promoting intercultural understanding, and preparing students for the challenges of the 21st century. The institutions that successfully navigate the complexities of international collaboration will be well-positioned to lead in an era where global perspectives are not just beneficial, but essential.
Questions 6-13
Complete the sentences below.
Choose NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from the passage for each answer.
-
Global partnerships in higher education represent a ____ ____ in educational approaches.
-
The combination of diverse perspectives in international collaborations often leads to ____ ____.
-
Academic mobility is enhanced through exchange programs and ____ ____ ____.
-
Virtual mentoring has helped to break down ____ ____ in global education.
-
One concern about global partnerships is the potential for ____ ____ from developing countries.
-
Some institutions are creating ____ ____ in partner countries to balance knowledge exchange.
-
____ ____ initiatives aim to improve educational infrastructure in developing nations.
-
____ ____ technology may offer immersive international experiences without physical travel.
Passage 3 – Hard Text
The proliferation of global partnerships in higher education has ushered in an era of unprecedented academic collaboration, transcending geographical and cultural boundaries. These alliances, while offering myriad benefits, also present complex challenges that necessitate a nuanced understanding of their implications for the future of tertiary education worldwide.
At the forefront of these partnerships is the quest for knowledge creation and dissemination on a global scale. Universities engaged in transnational collaborations are increasingly focusing on interdisciplinary research that addresses pressing global issues. This approach not only leverages the collective expertise of diverse academic communities but also fosters a more holistic understanding of complex problems. For instance, research on sustainable development now frequently involves collaboration between environmental scientists, economists, sociologists, and policymakers from multiple countries, leading to more comprehensive and actionable insights.
The impact of these partnerships extends beyond academia, influencing economic development and innovation ecosystems. Many collaborative programs now include industry partnerships, creating a triumvirate of university-industry-government cooperation known as the “Triple Helix” model. This model facilitates the transfer of knowledge from academic research to practical applications, spurring innovation and economic growth. Countries with emerging economies are particularly benefiting from this approach, as it allows them to leapfrog stages of technological development by partnering with institutions at the cutting edge of research and innovation.
However, the landscape of global partnerships is not without its pitfalls. The asymmetry of resources and influence between institutions from developed and developing nations can lead to unequal partnerships, potentially exacerbating rather than mitigating global inequalities in higher education. There is a risk of academic imperialism, where the educational models and research priorities of Western institutions dominate, potentially marginalizing local knowledge systems and cultural contexts.
How digital storytelling is being used in mental health education demonstrates how global partnerships can address sensitive topics across cultures. This approach highlights the need for culturally sensitive collaboration in higher education.
Moreover, the quality assurance of transnational education programs remains a significant challenge. The diversity of national accreditation systems and academic standards complicates the process of ensuring consistent quality across international partnerships. This has led to calls for the development of global quality frameworks that can provide a common standard for assessing the efficacy and value of international higher education collaborations.
The digital revolution has been a double-edged sword for global partnerships in higher education. While it has facilitated easier communication and collaboration, it has also raised concerns about data privacy and intellectual property rights in cross-border academic exchanges. Institutions must navigate complex legal and ethical landscapes to ensure that their partnerships are not only productive but also protective of individual and institutional rights.
Looking to the future, the sustainability of global partnerships in higher education will likely depend on their ability to adapt to changing geopolitical dynamics and technological advancements. The concept of “glocalization” – adapting global educational models to local contexts – is gaining traction as a way to ensure that international collaborations remain relevant and beneficial to all parties involved.
How global migration shapes educational policies is another critical factor influencing the evolution of these partnerships. As student and academic mobility increases, institutions must develop strategies to accommodate diverse educational backgrounds and cultural perspectives.
In conclusion, while global partnerships in higher education offer tremendous potential for advancing knowledge, fostering innovation, and promoting intercultural understanding, they also require careful navigation of complex ethical, cultural, and practical challenges. The institutions that succeed in this arena will be those that can balance the global and the local, the traditional and the innovative, creating partnerships that are truly equitable, sustainable, and transformative in their impact on higher education and society at large.
Questions 14-20
Do the following statements agree with the information given in the passage?
Write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
-
Interdisciplinary research in global partnerships often leads to more comprehensive solutions to global problems.
-
The “Triple Helix” model always results in successful technology transfer from universities to industries.
-
There is a risk that partnerships between institutions from developed and developing countries could increase educational inequalities.
-
All countries have agreed on a single global quality framework for assessing international higher education collaborations.
-
The digital revolution has only had positive effects on global partnerships in higher education.
-
The concept of “glocalization” involves adapting global educational models to suit local contexts.
-
Global partnerships in higher education will become less important in the future due to geopolitical challenges.
Answer Key
- C
- B
- C
- C
- B
- fundamental shift
- groundbreaking discoveries
- joint degree offerings
- geographical barriers
- brain drain
- regional hubs
- Capacity-building
- Virtual reality
- TRUE
- FALSE
- TRUE
- FALSE
- FALSE
- TRUE
- NOT GIVEN
This IELTS Reading practice test on “Global Partnerships in Higher Education” covers various aspects of international collaboration in tertiary education. It highlights the benefits, challenges, and future trends in this field, providing a comprehensive overview that aligns with typical IELTS exam content. Remember to practice regularly with diverse topics to improve your reading skills and expand your vocabulary for the IELTS test.