The IELTS Reading test often features passages on innovative educational approaches. One such topic that has gained prominence is the concept of flipped classrooms and how they are reshaping learning dynamics. This article presents a comprehensive IELTS Reading practice test focused on this subject, complete with passages, questions, and answers to help you prepare effectively for your exam.
The rise of remote learning platforms in higher education has paved the way for new teaching methodologies like flipped classrooms. Let’s explore this concept through a series of IELTS-style reading passages and questions.
Passage 1 – Easy Text
The Flipped Classroom Revolution
The traditional classroom model, where teachers lecture and students complete homework assignments outside of class, has been a cornerstone of education for centuries. However, a new approach called the “flipped classroom” is gaining traction and revolutionizing the way students learn. In a flipped classroom, the conventional order of teaching and learning activities is reversed. Students are introduced to new content through pre-recorded lectures or reading materials at home, while class time is devoted to discussions, problem-solving, and hands-on activities.
This innovative method was pioneered by Jonathan Bergmann and Aaron Sams, two high school chemistry teachers from Colorado, USA. They began recording their lectures for students who missed classes and soon realized the potential of this approach for all students. By providing lecture content beforehand, they found that classroom time could be used more effectively for interactive learning experiences.
The flipped classroom model offers several advantages. Firstly, it allows students to learn at their own pace, pausing and rewinding lectures as needed. This self-paced learning can be particularly beneficial for students who struggle to keep up in traditional lecture settings. Secondly, it frees up class time for more engaging activities, such as group projects, discussions, and problem-based learning. This increased interaction can lead to deeper understanding and better retention of material.
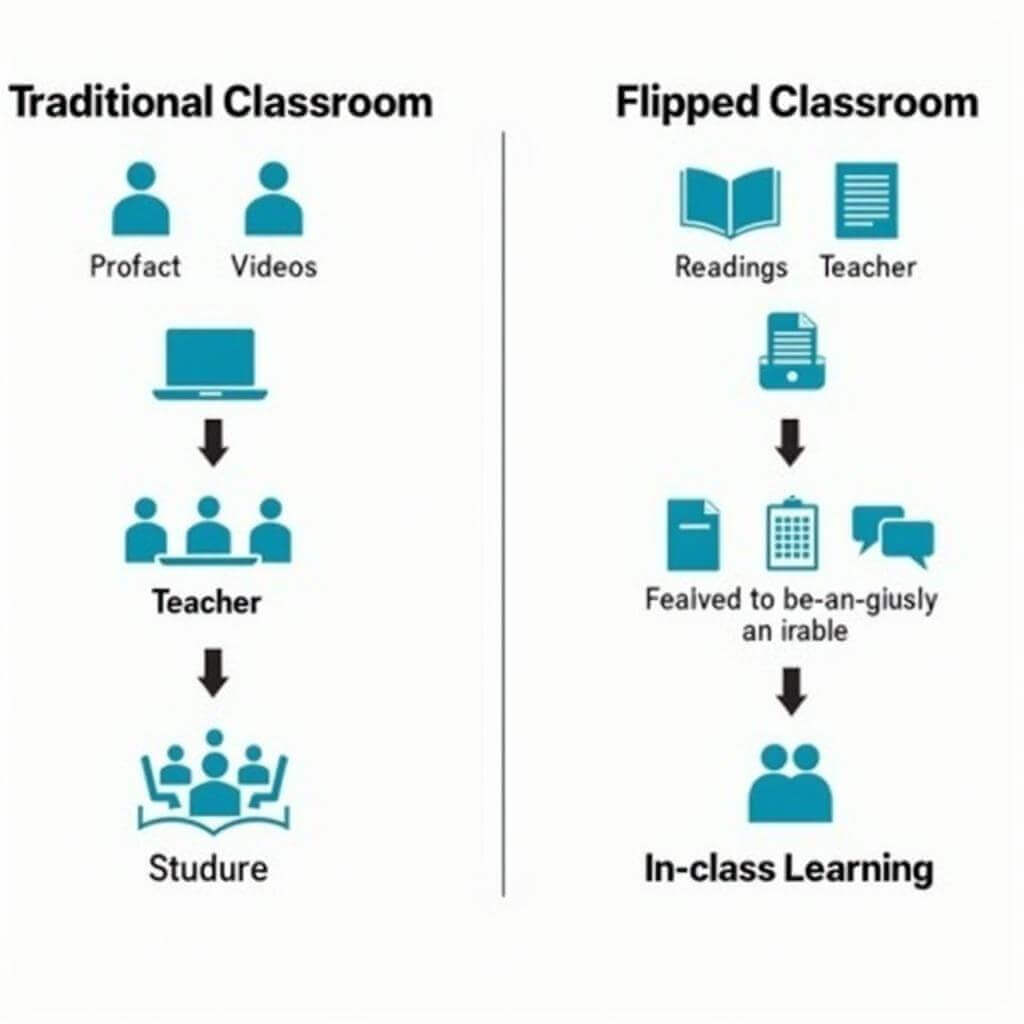
However, the flipped classroom approach is not without challenges. It requires significant preparation from teachers, who must create or curate high-quality video lectures and learning materials. Students, too, must adapt to taking more responsibility for their learning outside of class. Additionally, access to technology can be a barrier for some students, potentially exacerbating existing educational inequalities.
Despite these challenges, many educators and students report positive outcomes from flipped classrooms. Studies have shown improvements in student engagement, academic performance, and critical thinking skills. As technology continues to advance and become more accessible, the flipped classroom model may well represent the future of education.
Questions 1-7
Do the following statements agree with the information given in the reading passage?
Write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
- The flipped classroom approach is a completely new concept in education.
- Jonathan Bergmann and Aaron Sams initially recorded lectures for absent students.
- In a flipped classroom, all learning takes place outside of class time.
- The flipped classroom model allows students to learn at their own speed.
- Teachers find it easier to prepare materials for a flipped classroom than for a traditional one.
- All students have reported positive outcomes from flipped classrooms.
- The flipped classroom model may become more common as technology improves.
Questions 8-10
Complete the sentences below.
Choose NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from the passage for each answer.
- In a traditional classroom, students typically complete ____ assignments outside of class.
- The flipped classroom model can be particularly helpful for students who find it difficult to ____ in conventional lecture environments.
- One potential drawback of the flipped classroom approach is that it might ____ existing educational inequalities.
Passage 2 – Medium Text
Reshaping Learning Dynamics through Flipped Classrooms
The paradigm shift towards flipped classrooms is fundamentally altering the dynamics of learning in educational institutions worldwide. This innovative approach, which inverts the traditional teaching model, is not merely a technological trend but a comprehensive reimagining of the educational experience. By leveraging digital platforms and asynchronous learning techniques, flipped classrooms are fostering a more student-centric and interactive learning environment.
At the core of the flipped classroom model is the concept of active learning. Traditional passive learning, where students absorb information through lectures, is replaced with a more engaging approach. Students are expected to come to class having already familiarized themselves with the basic concepts through pre-recorded lectures or assigned readings. This prior exposure allows classroom time to be utilized for more cognitively demanding activities such as problem-solving, critical analysis, and collaborative projects.
The flipped model aligns well with contemporary learning theories, particularly constructivism. This theory posits that learners actively construct their understanding by integrating new information with their existing knowledge. In a flipped classroom, students have the opportunity to build their initial understanding independently, then refine and expand it through classroom interactions. This process of knowledge construction is further enhanced by the peer learning opportunities that flipped classrooms facilitate.
How online education is reshaping traditional learning is evident in the way flipped classrooms are changing student-teacher dynamics. The role of the teacher evolves from being a mere dispenser of knowledge to a facilitator of learning. This shift allows for more personalized instruction, as teachers can dedicate more time to individual student needs during class sessions. Moreover, the flipped model encourages students to take greater responsibility for their learning, fostering self-regulation and metacognitive skills.
However, the transition to a flipped classroom is not without challenges. It requires a significant investment of time and resources to create or curate high-quality digital content. There’s also the risk of exacerbating the digital divide, as not all students may have equal access to the necessary technology outside of school. Furthermore, the success of the flipped model heavily depends on student engagement with the pre-class materials, which can be difficult to ensure consistently.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of flipped classrooms are compelling. Research indicates that this approach can lead to improved learning outcomes, increased student satisfaction, and the development of crucial 21st-century skills such as critical thinking, collaboration, and digital literacy. As educational institutions continue to adapt to the changing needs of learners and society, the flipped classroom model represents a promising avenue for enhancing the quality and effectiveness of education.
The impact of flipped classrooms extends beyond academic performance. By encouraging active participation and collaborative learning, this model helps develop important soft skills such as communication, teamwork, and problem-solving. These skills are increasingly valued in the modern workplace, making the flipped classroom approach particularly relevant in preparing students for their future careers.
As the educational landscape continues to evolve, the flipped classroom model stands out as a powerful tool for reshaping learning dynamics. Its emphasis on active learning, personalized instruction, and the development of critical skills aligns well with the demands of the 21st-century knowledge economy. While challenges remain, the potential of flipped classrooms to transform education and better prepare students for the complexities of the modern world is undeniable.
Questions 11-15
Choose the correct letter, A, B, C, or D.
-
According to the passage, the flipped classroom model:
A) Is primarily a technological trend
B) Completely replaces traditional teaching methods
C) Reimagines the educational experience
D) Is only suitable for certain subjects -
In a flipped classroom, students are expected to:
A) Complete all learning activities during class time
B) Familiarize themselves with basic concepts before class
C) Listen to lectures during class time
D) Avoid using digital platforms for learning -
The role of the teacher in a flipped classroom:
A) Remains unchanged from traditional classrooms
B) Becomes less important
C) Shifts towards facilitating learning
D) Focuses solely on creating digital content -
One of the challenges of implementing flipped classrooms is:
A) Decreased student engagement
B) Lack of research on its effectiveness
C) Potential exacerbation of the digital divide
D) Reduced development of soft skills -
The passage suggests that flipped classrooms:
A) Are only effective for academic subjects
B) Hinder the development of communication skills
C) Are not suitable for preparing students for future careers
D) Can help develop important workplace skills
Questions 16-20
Complete the summary below.
Choose NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from the passage for each answer.
The flipped classroom model represents a 16) in education, moving away from passive learning towards a more 17) approach. This aligns with the theory of 18), which suggests that learners actively build their understanding. The model also promotes 19) learning opportunities and encourages students to develop 20)____ skills, which are crucial for managing their own learning process.
Passage 3 – Hard Text
The Transformative Impact of Flipped Classrooms on Educational Ecosystems
The advent of flipped classrooms represents a paradigmatic shift in educational methodologies, fundamentally altering the dynamics of knowledge acquisition and dissemination. This innovative approach, which inverts the traditional lecture-homework paradigm, is not merely a superficial change in instructional delivery but a profound reimagining of the entire educational ecosystem. By leveraging asynchronous learning modalities and digital pedagogies, flipped classrooms are catalyzing a transformation that extends far beyond the confines of individual institutions, potentially reshaping the broader landscape of education.
At its core, the flipped classroom model is predicated on the principle of active learning, a pedagogical approach that places students at the center of the educational process. This student-centric paradigm represents a significant departure from the passive, lecture-based model that has dominated education for centuries. In a flipped classroom, the onus of initial content exposure is shifted to pre-class activities, typically in the form of video lectures or curated readings. This reallocation of instructional time allows for a more judicious utilization of face-to-face interactions, focusing on higher-order cognitive tasks such as analysis, synthesis, and evaluation.
The theoretical underpinnings of the flipped classroom model align closely with constructivist learning theory, which posits that knowledge is actively constructed by learners rather than passively absorbed. By providing students with the opportunity to engage with content independently before class, flipped classrooms create a scaffold for knowledge construction. This initial exposure serves as a foundation upon which more complex understanding can be built through collaborative activities and guided instruction during class time. The model thus facilitates a synergistic integration of individual and collective learning experiences.
The impact of e-learning on traditional education systems is particularly evident in the context of flipped classrooms. This approach necessitates a fundamental reconfiguration of the roles of both educators and learners. Teachers transition from being primary sources of information to facilitators of learning experiences, guiding students through the process of knowledge construction and application. This shift demands a high degree of pedagogical dexterity, requiring educators to develop new skills in content creation, technology integration, and adaptive instruction.
Concomitantly, students are called upon to assume greater agency in their learning journey. The flipped model demands a higher level of self-regulation and metacognitive awareness from learners, who must navigate the pre-class content independently and come prepared to engage in more complex tasks during class time. This increased responsibility fosters the development of critical 21st-century skills such as information literacy, digital fluency, and autonomous learning capabilities.
However, the implementation of flipped classrooms is not without its challenges. The model requires a significant investment in technological infrastructure and content development, which may strain institutional resources. Moreover, there is a risk of exacerbating existing educational inequities, as the success of the flipped approach is often contingent upon students’ access to reliable internet connectivity and appropriate devices outside of the classroom. These potential barriers underscore the need for a thoughtful and equitable approach to implementation.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of flipped classrooms are substantial and far-reaching. Research indicates that this approach can lead to improved learning outcomes, increased student engagement, and enhanced development of higher-order thinking skills. Furthermore, the flipped model’s emphasis on active learning and collaborative problem-solving aligns closely with the demands of the modern knowledge economy, potentially enhancing students’ preparedness for future professional endeavors.
The impact of flipped classrooms extends beyond individual learning outcomes, potentially catalyzing broader systemic changes in education. By challenging traditional notions of instructional time and space, this model opens up new possibilities for flexible learning environments and personalized education pathways. It also has the potential to foster greater collaboration between educators, as the creation and sharing of digital content encourage the development of professional learning communities.
Moreover, the flipped classroom model intersects with other emerging trends in education, such as competency-based learning and adaptive technologies. This convergence creates opportunities for more nuanced and responsive educational experiences that can adapt to individual learner needs and preferences. As these synergies continue to evolve, they may precipitate a more comprehensive reimagining of educational structures and practices.
In conclusion, the flipped classroom model represents a powerful catalyst for educational transformation. Its potential to reshape learning dynamics, foster critical skills, and adapt to the needs of the digital age positions it as a significant force in the ongoing evolution of education. While challenges remain, the trajectory of flipped classrooms suggests a future where learning is more active, engaging, and aligned with the complex demands of our rapidly changing world.
How traditional education systems adapt to digital transformation is exemplified by the increasing adoption of flipped classrooms, showcasing the potential for innovation within established educational frameworks.
Questions 21-26
Complete the sentences below.
Choose NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from the passage for each answer.
- The flipped classroom model represents a ____ in educational methodologies.
- In a flipped classroom, face-to-face interactions focus on ____ cognitive tasks.
- The flipped classroom model aligns with ____ learning theory.
- Teachers in flipped classrooms need to develop ____ to effectively guide students.
- The success of flipped classrooms often depends on students’ access to ____ outside of the classroom.
- Flipped classrooms may lead to the development of ____ between educators.
Questions 27-30
Do the following statements agree with the claims of the writer in the reading passage?
Write
YES if the statement agrees with the claims of the writer
NO if the statement contradicts the claims of the writer
NOT GIVEN if it is impossible to say what the writer thinks about this
- Flipped classrooms completely eliminate the need for traditional lectures.
- The implementation of flipped classrooms requires significant investment in technology and content development.
- All students benefit equally from the flipped classroom model, regardless of their access to technology.
- The flipped classroom model has the potential to influence broader changes in educational systems.
Answer Key
Passage 1
- FALSE
- TRUE
- FALSE
- TRUE
- FALSE
- NOT GIVEN
- TRUE
- homework
- keep up
- exacerbate
Passage 2
- C
- B
- C
- C
- D
- paradigm shift
- active
- constructivism
- peer
- metacognitive
Passage 3
- paradigmatic shift
- higher-order
- constructivist
- pedagogical dexterity
- reliable internet connectivity
- professional learning communities
- NO
- YES
- NO
- YES
This comprehensive IELTS Reading practice test on flipped classrooms and learning dynamics provides a thorough exploration of the topic while testing various reading skills. Remember to practice regularly and analyze your performance to improve your IELTS Reading score.