Introduction: Why Diagram Description Matters in IELTS
In the IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, your ability to accurately and effectively describe visual information is tested. This often involves analyzing and summarizing data presented in diagrams, a skill crucial for academic success and beyond.
This comprehensive guide will equip you with the essential strategies and vocabulary to confidently tackle IELTS Task 1 diagram descriptions, ensuring you achieve your desired band score.
Understanding IELTS Task 1 Diagrams
Before delving into the writing process, it’s crucial to understand the types of diagrams you might encounter:
Types of Diagrams:
- Process diagrams: Illustrate how something works or is made through a series of stages.
- Manufacturing/Production diagrams: Show the steps involved in creating a product.
- Technical diagrams: Explain the workings of a device or system using labelled parts.
- Cyclical diagrams: Depict a process that repeats itself, such as the water cycle.
The Art of Describing Diagrams Effectively
1. Analyze the Diagram Carefully:
- Identify the main purpose: What is the diagram trying to show?
- Note key features: What are the most significant elements and their relationships?
- Look for trends, changes, and comparisons: How do the different parts of the diagram interact?
2. Structure Your Response:
- Introduction (Paraphrase): Briefly describe the diagram’s main purpose in your own words.
- Overview (Summary): Highlight the key stages, trends, or features without going into detail.
- Body Paragraphs (Detailed Description): Provide a clear and organized description of the process or information presented in the diagram. Use chronological order for process diagrams and group similar information for other types.
- Conclusion (Optional): Summarize the most important findings, but avoid introducing new information.
3. Use Precise Vocabulary and Grammar:
- Vocabulary for describing trends: Increase, decrease, rise, fall, fluctuate, remain stable, peak, plateau, trend upwards/downwards.
- Vocabulary for describing stages: Initially, subsequently, following this, at this point, simultaneously, concurrently.
- Connectors and sequencers: Firstly, secondly, furthermore, in addition, meanwhile, finally.
- Passive voice: Use the passive voice when describing processes where the action is more important than the agent (e.g., “The liquid is then heated to 100 degrees Celsius.”)
Example: Describing a Process Diagram
Let’s analyze an example of a process diagram and apply these strategies:
Sample Answer:
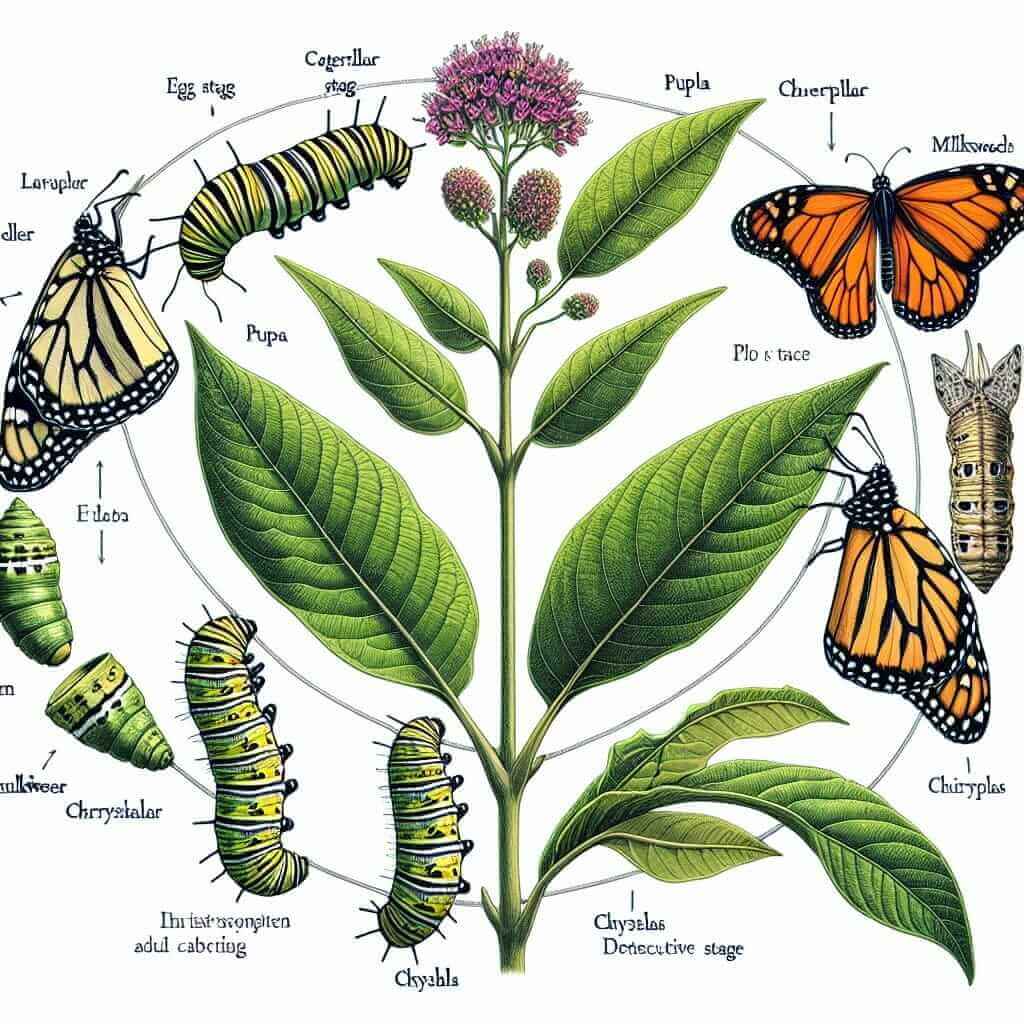
The diagram illustrates the life cycle of a monarch butterfly, from its initial stage as an egg to its final form as a mature butterfly.
Overall, the process involves four main stages, beginning with the laying of an egg on a milkweed plant and culminating in the emergence of an adult butterfly capable of reproduction.
Initially, a female butterfly lays an egg on the leaf of a milkweed plant. After approximately four days, the egg hatches, and a larva, also known as a caterpillar, emerges. The caterpillar’s primary activity is feeding on the milkweed leaves to fuel its growth. This larval stage lasts for around two weeks. Subsequently, the caterpillar enters the pupa stage, where it forms a protective casing called a chrysalis around itself. Inside the chrysalis, a remarkable transformation occurs over a period of 10 to 14 days. Finally, the chrysalis splits open, and a fully developed adult butterfly emerges. The adult butterfly then continues the life cycle by mating and laying eggs, thus starting the process anew.
Tips for Success:
- Practice regularly: Familiarize yourself with different diagram types and practice describing them within the time limit.
- Use accurate data: Pay close attention to the details and numbers presented in the diagram.
- Avoid interpreting data: Focus on describing what you see, not on drawing conclusions or expressing opinions.
- Proofread carefully: Check for any errors in grammar, vocabulary, and spelling.
Conclusion:
Mastering IELTS Task 1 diagram descriptions requires a combination of analytical skills, precise language, and effective organization. By understanding the different diagram types, following a clear structure, and utilizing specific vocabulary, you can confidently approach this task and enhance your overall IELTS writing score. Remember, consistent practice is key to achieving success in this section of the exam.