The word “subcutaneous” (/ˌsʌb.kjuːˈteɪ.ni.əs/), often abbreviated as “subQ” or “SC,” is an adjective commonly encountered in medical contexts. Understanding this term and its related vocabulary is crucial for achieving a high IELTS score, especially in the Listening and Reading sections, and potentially in the Writing and Speaking sections as well.
Here are some synonyms for subcutaneous:
- Hypodermic: (adj.) /ˌhaɪ.poʊˈdɜː.mɪk/ relating to the region immediately beneath the skin
- Under the skin: (phrase) situated or applied below the surface of the skin
Understanding “Subcutaneous”
Definition and Usage
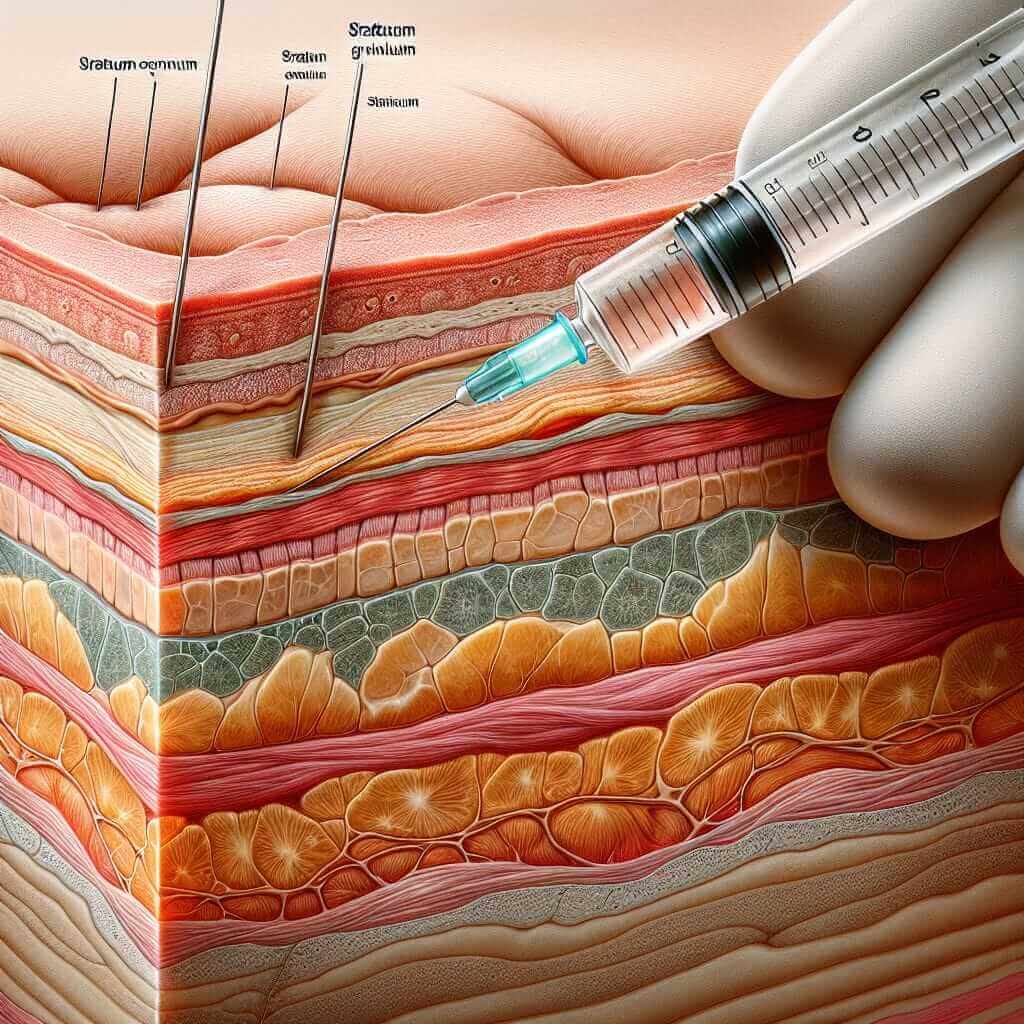
“Subcutaneous” refers to the layer of tissue found just beneath the skin. This layer is primarily composed of fat and connective tissue, and it plays a vital role in:
- Insulation: Maintaining body temperature
- Energy storage: Storing excess calories as fat
- Protection: Cushioning and protecting underlying muscles and organs
In medical contexts, “subcutaneous” often describes the administration of medication or fluids:
- Subcutaneous injection: Injecting a substance into the subcutaneous layer, allowing for slow and steady absorption into the bloodstream.
- Subcutaneous implant: Placing a device, like a contraceptive implant, beneath the skin.
IELTS Relevance
“Subcutaneous” frequently appears in IELTS texts and audio related to:
- Biology: Discussing skin structure, tissue types, or drug delivery mechanisms.
- Healthcare: Describing medical procedures, treatments, or drug administration methods.
- Pharmaceuticals: Explaining drug properties, administration routes, or potential side effects.
Applying “Subcutaneous” in IELTS
Listening Section
You might hear “subcutaneous” in a lecture about the human body or in a conversation between a doctor and a patient discussing treatment options.
Example:
- Narrator: “The doctor explained that a subcutaneous injection would deliver the medication slowly and steadily…”
Reading Section
You might encounter “subcutaneous” in a passage about diabetes management or the development of new drug delivery systems.
Example:
- Passage excerpt: “Subcutaneous insulin pumps offer a more convenient and discreet alternative to multiple daily injections for patients with type 1 diabetes.”
Writing Section
You could use “subcutaneous” when describing a graph or chart that presents data on injection techniques or drug absorption rates.
Example:
- Your response: “The graph clearly illustrates that subcutaneous administration results in a slower and more sustained drug release profile compared to intravenous administration.”
Speaking Section
You might use “subcutaneous” when discussing your health, medical experiences, or opinions on healthcare advancements.
Example:
- Your response: “I believe that subcutaneous implants offer a promising solution for long-term contraception due to their effectiveness and convenience.”
Collocations and Idioms
While there aren’t specific idioms using “subcutaneous,” it’s important to be familiar with common collocations:
- Subcutaneous fat: Refers to the layer of fat beneath the skin
- Subcutaneous injection site: The specific location where a subcutaneous injection is given
- Subcutaneous needle: A type of needle designed for subcutaneous injections
Conclusion
Mastering the term “subcutaneous” and its related vocabulary is essential for navigating medical and healthcare-related topics in the IELTS exam. By understanding its meaning, usage, and relevance across different sections, you can confidently approach the exam and demonstrate your English language proficiency. Remember to practice using “subcutaneous” in various contexts to solidify your understanding and enhance your ability to achieve your desired IELTS score.