The IELTS Reading section is an essential part of the IELTS exam. This section tests your ability to read and understand a wide range of texts, including topics like climate change. Climate change is a highly prevalent topic that has been seen in past IELTS exams, making it a crucial area for preparation. In this article, we will delve into the consequences of climate change on freshwater availability, providing a comprehensive Reading practice passage and questions to help you excel in your IELTS exam.
Practice Reading Passage: Medium Text
The Impact of Climate Change on Freshwater Availability
Climate change has become one of the most pressing issues of our time, significantly affecting various aspects of our environment, including freshwater resources. Freshwater is vital for human survival, agriculture, industry, and ecosystems. However, the consequences of climate change on freshwater availability are profound and multifaceted.
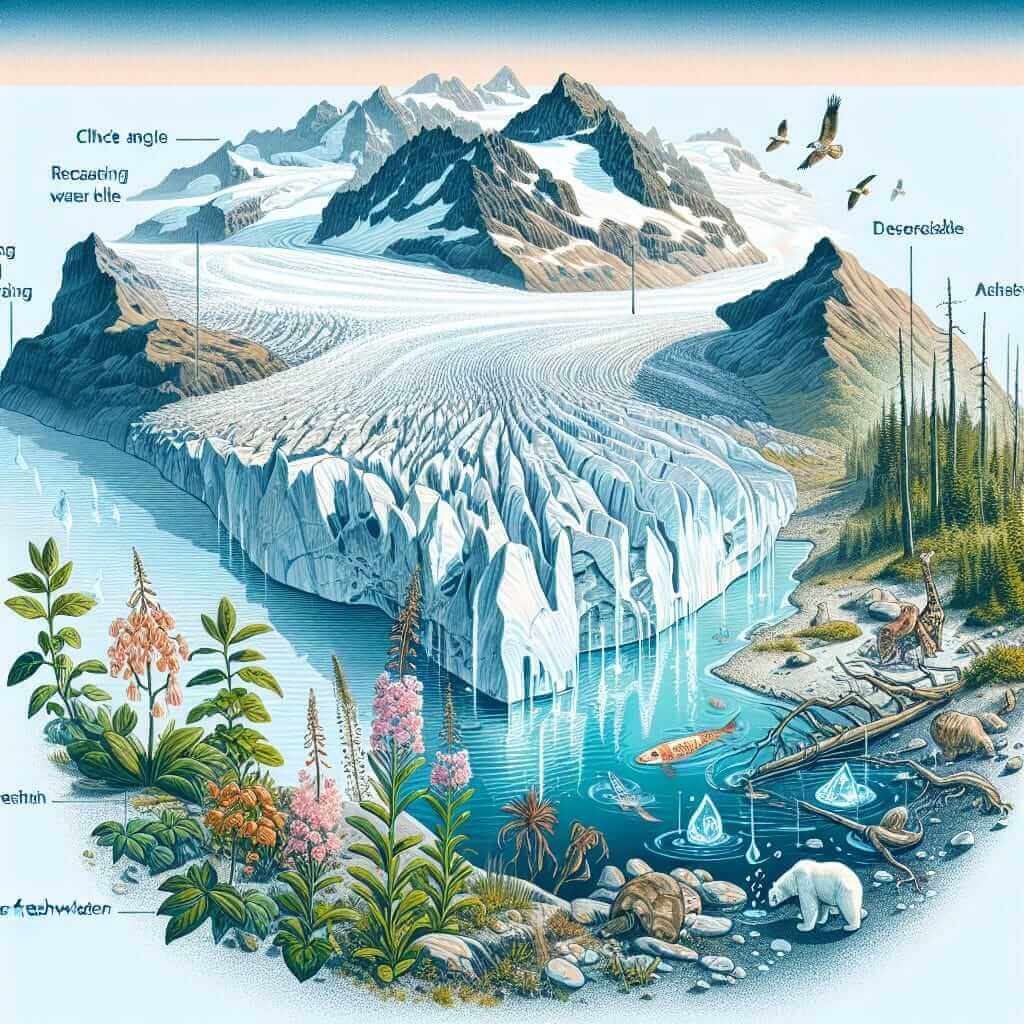
One of the primary impacts of climate change on freshwater resources is the alteration of hydrological cycles. Rising global temperatures lead to increased evaporation rates, intensifying the water cycle. This results in unpredictable precipitation patterns, such as more severe droughts and floods, which directly affect freshwater availability. Regions relying heavily on predictable rainfall, such as parts of Africa and Asia, are particularly vulnerable.
Another consequence is the melting of glaciers and polar ice caps, which serve as essential freshwater reservoirs. As global temperatures rise, these ice masses shrink, reducing the volume of freshwater they supply. This loss is particularly alarming for regions dependent on glacial meltwater, such as the Himalayas, where significant populations depend on this resource for drinking water and agriculture.
Climate change also exacerbates the salinization of freshwater sources. Rising sea levels, driven by the thermal expansion of seawater and melting ice, lead to the encroachment of saltwater into freshwater aquifers and coastal basins. This process, known as saltwater intrusion, diminishes the quality of freshwater and makes it unsuitable for consumption and irrigation.
Furthermore, warmer temperatures increase the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events like hurricanes and typhoons. These events can disrupt water infrastructure, contaminate freshwater supplies, and hinder access to clean water. Island nations and coastal regions are particularly at risk of experiencing severe freshwater shortages in the aftermath of such events.
In conclusion, the consequences of climate change on freshwater availability are complex and far-reaching. Changes in hydrological cycles, glacial melt, salinization, and extreme weather events pose significant challenges to ensuring a stable and adequate supply of freshwater. Addressing these issues requires global collaboration, sustainable water management practices, and concerted efforts to mitigate climate change.
IELTS Reading Practice Questions
Questions 1-5: Multiple Choice
Choose the correct letter, A, B, C, or D.
-
What is one of the primary impacts of climate change on freshwater resources?
- A. Increased rainfall globally.
- B. Alteration of hydrological cycles.
- C. Decreased evaporation rates.
- D. Expanding glacial ice masses.
-
Which regions are particularly vulnerable to unpredictable precipitation patterns caused by climate change?
- A. North America and Europe
- B. Africa and Asia
- C. Australia and South America
- D. Antarctica and Arctic
-
How does the melting of glaciers affect freshwater availability?
- A. It increases the volume of freshwater globally.
- B. It reduces the volume of freshwater they supply.
- C. It stabilizes freshwater reservoirs.
- D. It has no significant impact on freshwater.
-
What process leads to the salinization of freshwater sources?
- A. Ice caps expanding
- B. Increased freshwater precipitation
- C. Saltwater intrusion
- D. Enhanced evaporation rates
-
Which regions are most affected by extreme weather events like hurricanes and typhoons in terms of freshwater availability?
- A. Inland regions
- B. Polar regions
- C. Island nations and coastal regions
- D. Mountainous regions
Questions 6-10: True/False/Not Given
-
Climate change leads to predictable precipitation patterns.
True / False / Not Given -
The Himalayas rely on glacial meltwater for freshwater supplies.
True / False / Not Given -
Rising sea levels are primarily caused by the expansion of glacial ice.
True / False / Not Given -
Saltwater intrusion improves the quality of freshwater sources.
True / False / Not Given -
Sustainable water management practices are necessary to address freshwater availability issues.
True / False / Not Given
Answer Keys
-
B. Alteration of hydrological cycles.
-
B. Africa and Asia
-
B. It reduces the volume of freshwater they supply.
-
C. Saltwater intrusion
-
C. Island nations and coastal regions
-
False
-
True
-
Not Given
-
False
-
True
Common Mistakes in IELTS Reading
When working on the IELTS Reading section, students often face several common pitfalls. Misinterpreting the question type, failing to manage time effectively, and overlooking key details in the text are typical errors. Make sure to read each question carefully, understand what is being asked, and allocate your time wisely. Practice skimming and scanning techniques to quickly find relevant information.
Vocabulary
- Hydrological (adj.) /ˌhaɪdrəˈlɒdʒɪk(ə)l/: relating to the science of hydrology.
- Example: Changes in the hydrological cycle can affect water availability.
- Precipitation (n.) /prɪˌsɪpɪˈteɪʃən/: any form of water – liquid or solid – falling from the sky.
- Example: Unpredictable precipitation patterns have increased due to climate change.
- Salinization (n.) /ˌsælɪˌnaɪˈzeɪʃən/: the process of increasing the salt content in something.
- Example: Rising sea levels cause the salinization of freshwater aquifers.
- Intrusion (n.) /ɪnˈtruːʒən/: the act of entering where one is not welcome or invited.
- Example: Saltwater intrusion affects freshwater quality along coastal regions.
- Glacial (adj.) /ˈɡleɪʃəl/: relating to or derived from a glacier.
- Example: Glacial meltwater is crucial for freshwater supplies in certain regions.
Grammar Focus
Conditional Sentences – Third Conditional
- Structure: If + Past Perfect, would have + Past Participle
- Usage: To express a hypothetical past situation and its result.
- Example: If the climate had not changed, we wouldn’t have faced severe freshwater shortages.
Example
- If the glaciers had remained stable, there would have been enough freshwater for agricultural use.
Tips for a High IELTS Reading Score
- Practice Regularly: Consistently practicing reading passages similar to IELTS tests will improve your comprehension skills.
- Develop Skimming and Scanning Techniques: These techniques help in quickly locating information within the text.
- Improve Vocabulary: A strong vocabulary will assist in understanding complex texts easily.
- Understand Question Types: Familiarize yourself with different question types and effective strategies to tackle them.
For more practice on how climate change affects water availability, check out What are the Effects of Climate Change on Global Water Availability and How is Climate Change Impacting Global Freshwater Availability.
By integrating these strategies and understanding the topic thoroughly, you’ll be better prepared to tackle questions related to climate change and freshwater availability in your IELTS exam. Good luck!