As an IELTS instructor with over 20 years of experience, I’ve encountered countless students who underestimate the power of vocabulary in boosting their speaking scores. A strong vocabulary not only helps you articulate your thoughts clearly but also demonstrates your command of the English language. One area where specific vocabulary can truly shine is when discussing architecture, a topic that often arises in the IELTS Speaking test.
This article will explore the question “Why pagodas don’t fall down” within the context of IELTS Speaking. We will delve into the relevant vocabulary, discuss how to effectively incorporate it into your responses, and provide practical tips to help you achieve your desired score.
The Significance of Architectural Vocabulary in IELTS Speaking
Imagine yourself in the IELTS Speaking test. You’ve been asked to describe a famous landmark in your country, and you choose a beautiful, ancient pagoda. But as you begin to speak, you find yourself struggling to find the right words to describe its unique features. This is where a strong architectural vocabulary comes in handy.
Knowing terms like “eaves,” “beams,” “columns,” and “foundations” not only allows you to provide precise descriptions but also demonstrates to the examiner your ability to use a range of vocabulary accurately and confidently.
Unlocking the Secrets: Why Pagodas Withstand the Test of Time
The seemingly simple question “Why pagodas don’t fall down” offers a fantastic opportunity to showcase your vocabulary related to architecture, engineering, and history. Let’s explore some key aspects and the vocabulary you can use:
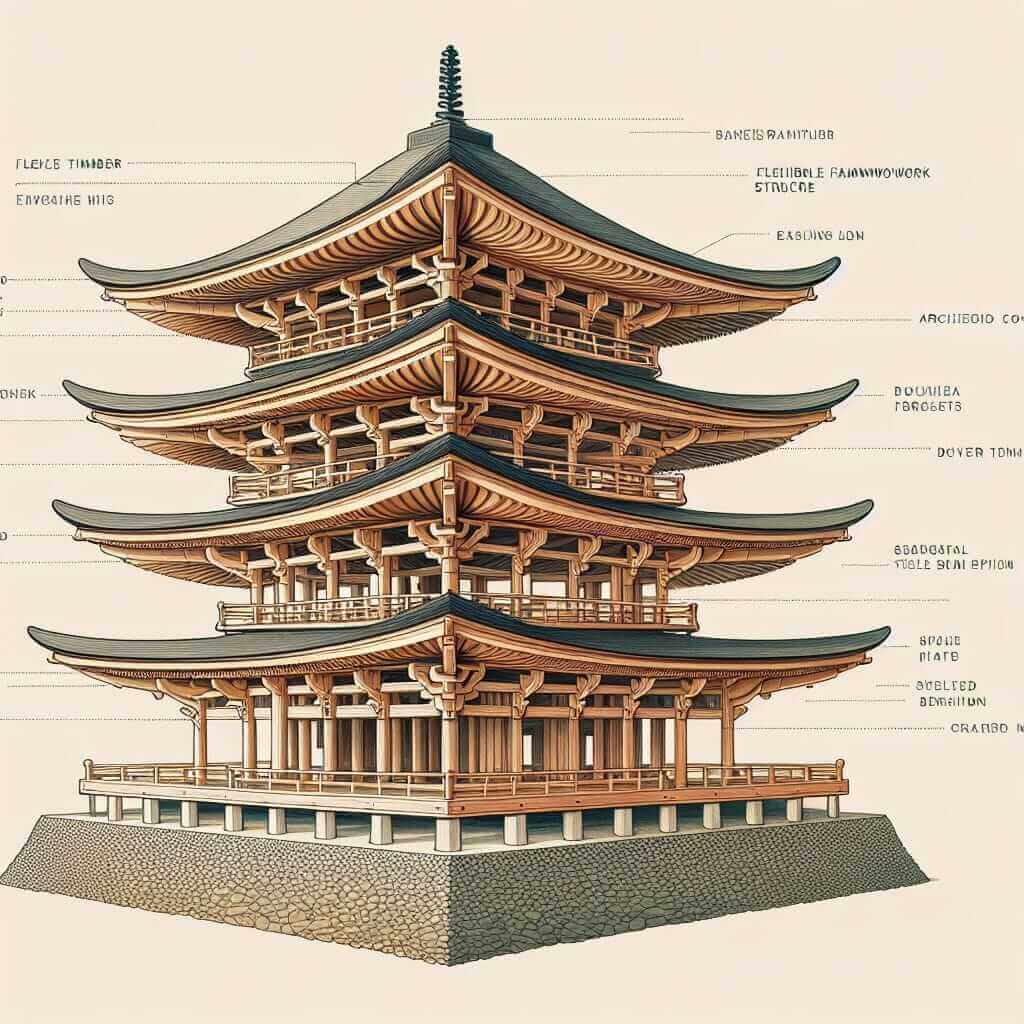
1. Structural Design and Materials:
-
Flexible Timber Framework: Pagodas, unlike rigid structures, are designed to sway with the wind due to their flexible timber frameworks. This flexibility helps dissipate energy during earthquakes and storms.
- Vocabulary: Tensile strength, compression, interlocking joints, wooden dowels, resilience.
-
Tiered Structure with Overhanging Eaves: The multiple tiers, each with their characteristic overhanging eaves, play a crucial role in distributing weight and providing stability.
- Vocabulary: Weight distribution, cantilevered eaves, pagoda tiers, diminishing size, balance.
-
Strong Foundations: Pagodas often rest on solid stone platforms or deep foundations, ensuring stability on various terrains.
- Vocabulary: Stone foundations, bedrock, anchoring, ground stability, soil composition.
2. Historical and Cultural Context:
- Trial and Error: Centuries of architectural experimentation and refinement have led to the development of pagoda designs that are remarkably resilient to natural disasters.
- Vocabulary: Architectural evolution, historical context, cultural significance, adaptation, traditional knowledge.
3. Example in IELTS Speaking:
Examiner: “Tell me about a famous landmark in your country.”
You: “One iconic landmark in my country is the [Name of Pagoda]. It’s a magnificent example of traditional pagoda architecture, known for its resilience. What’s fascinating is how these structures have withstood numerous earthquakes over the centuries. The secret lies in their flexible timber framework and tiered structure with overhanging eaves, which help distribute weight and withstand strong winds. The pagoda’s deep stone foundations also play a vital role in anchoring it firmly to the ground.”
Tips for Success:
- Build Your Vocabulary: Actively learn and practice using architectural terms. Use flashcards, vocabulary lists, and online resources to expand your knowledge.
- Practice Describing Structures: Find pictures of different architectural styles, including pagodas, and practice describing them using specific vocabulary.
- Record Yourself: Record yourself speaking to identify areas for improvement and track your progress in using vocabulary accurately and fluently.
Conclusion
Mastering relevant vocabulary is an essential ingredient for success in the IELTS Speaking test. By focusing on architectural terms and understanding the structural marvel of pagodas, you can demonstrate a strong command of the English language and impress your examiner. Remember, consistent practice and a keen eye for detail are key to achieving your desired score.